| JuLang 1 (CSS-N-3) Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile
中国JL-1(CSS-N-3)潜射弹道导弹 Date:2013-10-26 Source:internet By:globalmil Viewed: |

The JL-1 is China’s first solid-propellant and first submarine-launched ballistic missile. The missile design was also used to develop a land-based intermediate range ballistic missile (IRBM) DF-21 (CSS-5).JL-1是中国的第一种固体推进剂和第一种潜射弹道导弹。导弹设计也用来发展一种DF-21(CSS-5)型陆基中程弹道导弹(IRBM)。
Official name: JuLang 1 (JL-1)
NATO reporting name: CSS-N-3
Contractor: CASIC 4th Academy
Service status: In service
正式命名: 巨浪-1(JL-1)
北约代号: CSS-N-3
承包商: 中国航天科技集团公司第四研究院(航天动力技术研究院)
服役状态: 服役中
The JuLang 1 (NATO reporting name: CSS-N-3) is a two-stage, solid-propellant submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) developed for the PLA Navy’s nuclear-powered missile submarine (SSBN). 12 missiles have been deployed by a single Type 092 (NATO reporting name: Xia class) SSBN since the late 1980s. An improved variant, possibly designated JuLang 1A, was introduced in the late 1990s. The land-launched version of the missile is DongFeng 21.
巨浪-1(北约代号:CSS-N-3)是为PLA海军核动力导弹潜艇(SSBN)发展的一种二级、固体推进剂潜射弹道导弹(SLBM)。从1980年以后12枚导弹已经部署在仅有的一艘092型(北约代号:夏级)SSBN上。一种改进型,可能指定为巨浪-1A型,在1990年后期被采用。导弹的陆基型是东风-21型。
The JuLang 1 missile provides the PRC with the capability to strike back after enemy’s first attack using nuclear weapons. The deployment of the missiles on a submarine significantly increases their survivability, as even today finding a missile submarine prior to launch is proven to be very difficult. However, the JuLang 1’s limited range (1,700km) requires the submarine to leave Chinese waters to conduct a strike, which would significantly increase the possibility of being detected and intercepted by enemy anti-submarine forces. The PRC reportedly developed an improved model JuLang 1A featuring increased range of 2,500km. An ongoing SLBM development programme known as JuLang 2 with 8,000km range will replace the JuLang 1 in the future.
巨浪-1型导弹赋予中国在敌人第一波攻击之后使用核武器报复能力。在一艘潜艇上部署导弹重要地增加它们的生存性,因为即使在今天当一艘导弹潜艇发射之前发现它被证明是非常困难地。然而,巨浪-1型有限射程(1,700公里)需要潜艇离开中国水域实施打击,会严重增加被敌方反潜力量发现和拦截的可能性。中国根据传闻发展改良的巨浪-1A型特点是射程增加到2,500公里。一个不断前进的SLBM发展计划即巨浪-2型具有8,000公里射程将会替代巨浪-1型。

The JL-1 SLBM was first revealed to public in the 1984 national day military parade held in Beijing, but the test launch of the missile from the Type 092 Xia class nuclear missile submarine was not successful until September 1987.JL-1 SLBM在北京举行1984年国庆阅兵式期间被首次展示。但是从092型夏(Xia)级核导弹潜艇上进行的弹道测试发射直到1987年9月前没有成功。
Programme
PRC began its research on the solid-propellant rocket technology as early as 1956, under the suggestion of Dr Qian Xuesen, the father of Chinese missile and rocketry. By 1960, the PRC was able to produce small-size (65mm and 107mm diameter) solid rockets. By 1965, the 300mm-diameter solid rocket was successfully tested and PRC scientists began to work on a larger 1,400mm-diameter rocket. The latter became successful in December 1966, indicating that the country possessed necessary technology to develop a solid-propellant missile.
计划
在中国导弹和火箭之父钱学森博士提议下,中国在1956年开始自己的固体推进剂火箭技术方面的研究。1960年之前,中国能够生产小型(65毫米和107毫米直径)固体火箭。1965年之前,300毫米直径固体火箭被成功地测试而且中国科学家开始致力于一枚大型1,400毫米直径火箭。在1966年12月获得成功,表明中国具有了发展一枚固体推进剂导弹必需的技术。
The SLBM development was initiated in March 1967 for the Type 092 SSBN in development. The development programme skipped the single-stage missile and started with a more complex two-stage design, which offers longer range but is more technologically challenging. The proposed JuLang 1 missile design was approved by the PLA Navy in October 1967, and technical specifications were issued in 1968. In 1970, Huang Wei-Lu was appointed as the chief designer of the JuLang 1 SLBM.
潜射弹道导弹(SLBM)发展在1967年3月开始用于092型SSBN。发展计划跨过单级导弹并且从更复杂的两级设计开始,提供更远射程但更具有科技挑战性。提议的巨浪-1型导弹设计在1967年10月获PLA海军批准,技术规格在1968年发布。在1970年,黄纬禄(Huang Wei-Lu)被任命为巨浪-1型SLBM主设计师。
The JuLang 1 designer decided to adopt the gas-propelled ‘cold-launch’ technique. In order to test the underwater launch mechanism, the design team carried out several hundred times of simulated launch using scaled missile mock-ups in water pool. In October 1972, a full-sized mock-up was successfully launched from a submerged Type 031 (Golf class) diesel-electric missile submarine hull No. 200.
巨浪-1型设计师决定采用气体弹射‘冷-发射’技术。为了要试验在水下的发射机制,设计队伍在水池内采用仿真导弹模型进行了几百次模拟发射。在1972年10月,一枚标准尺寸的仿真模型成功地从水下一艘031型(高尔夫级)柴电导弹潜艇(弦号200)发射。
By the late 1970s, the PRC had made breakthrough in a number of SLBM-associated technologies, including the lightweight nuclear warhead (600~700kg) developed by 14 Nuclear Institute; the guidance system developed by 717 Shipbuilding Institute; the onboard computer was developed by 771 Space Institute; the solid-propellant rocket motor by 4th Space Academy, the SLBM launch system developed by 701 Shipbuilding Institute, the inertial/celestial/satellite guidance system developed by 707 Shipbuilding Institute. The missile prototype was built by 211 Factory and 307 Factory. The construction of an SLBM test site with underwater communication and observation facilities and land-based missile tracking and telemetry facilities was finished in the early 1980s.
在1970年,中国在许多SLBM相关技术上获得突破性进展,包括轻型核弹头(600~700公斤)由核工业第十四研究所发展,制导系统由中船重工717研究所(华中光电技术研究所)发展;舰载计算机由航天771所(西安微电子技术研究所(九院))发展;固体火箭发动机由第四空间研究院(航天动力技术研究院)发展,发射系统由中船重工701研究所(武汉船舶设计研究所)发展,惯性/天文/星形制导系统由中船重工707研究所(天津航海仪器研究所)发展。导弹原型由211工厂(首都航天机械公司(航天一院211厂))和307工厂(航天科工四院307厂;南京晨光集团有限责任公司)制造。建立一个SLBM试验基地,水下通信和观察设备,陆基导弹跟踪和遥感勘测设备在1980年早期完成。
The test of the missile was to be carried out in three steps: land-based launch from a launch pad, land-based launch from a simulated launcher tube, and underwater launch from a submarine. The first successful flight test of the JuLang 1 missile from a land-based launch pad in the North Missile Test Base (Wuzhai Missile Test Centre) was carried out on 17 June 1981, followed by two successful launches from land-based launcher tubes in January and April 1982.
导弹测试分三个步骤进行:从一个发射台进行陆基发射,从一个仿真发射筒进行陆基发射和从一艘潜艇进行水下发射。在1981年6月17日巨浪-1型导弹从位于华北导弹试验基地(五寨导弹试验中心)的一个发射台上成功进行第一次飞行测试,在1982年1月和4月从陆基发射筒成功进行两次发射测试。
The underwater launch test was firstly carried out from the No.200 Golf class conventional submarine. The first flight test took place on 7 October 1982, but the missile lost control shortly after take-off. After some modifications on the missile, the second attempt on 12 October was successful. Preparation for the test launch from the Type 092 SSBN No.406 began in 1984. Between March and April 1984, four mock-up missiles were successfully launched from the No.200 submarine in order to test the underwater launch system. On 28 September 1985, a JuLang 1 missile launched from No.406 SSBN exploded in the midair shortly after the take-off. Two subsequent test launches also failed.
在水下发射测试首先从一艘弦号200“高尔夫”级常规潜艇上进行。第一次飞行测试在1982年10月7日进行,但是导弹在起飞后不久失去控制。在导弹上做了一些修正,第二次尝试在10月12日获得成功。在1984年开始准备从一艘弦号406 092型SSBN试射。1984年3月和4月之间,四枚仿真导弹用于测试水下发射系统从弦号200 潜艇成功发射。在1985年9月28日,一枚巨浪-1型导弹从弦号406 SSBN上起飞后不久在半空中爆炸。随后二次测试也发射失败。
Despite the failure, it was concluded that both the SSBN and its underwater launch system functioned perfectly during the launches. The programme planner decided to go ahead with the full-range flight test as scheduled. Preparation for the flight test began in late 1987. On 15 September 1988 at 09:00 local time, a naval task force comprising the No.406 SSBN and 30 various support ships departed from their base to the test range in the Yellow Sea. At 12:30, No.406 SSBN began to submerge and get ready for the launch. At 14:00, a JuLang 1 SLBM was launched from the submarine, and few moments later, the missile’s re-entry vehicle hit its target zone. A second flight test carried out on 27 September was also successful.
尽管失败,已经得出结论SSBN和它的水下发射系统两者在发射时候功能完善。计划规划者决定前进进行全射程飞行测试作为试验进度表。在1987年后期开始准备飞行测试。在当地时间1988年9月15日09:00,一个海军特遣队包括弦号406 SSBN和30艘各种不同的支援舰离开它们的基地到黄海测试水域。在12:30,弦号406 SSBN开始下潜并为发射做好准备。在14:00,巨浪-1型SLBM从潜艇发射,几分钟后导弹的再入运载具击中了它的目标区域。在9月27日第二次飞行测试也成功进行。
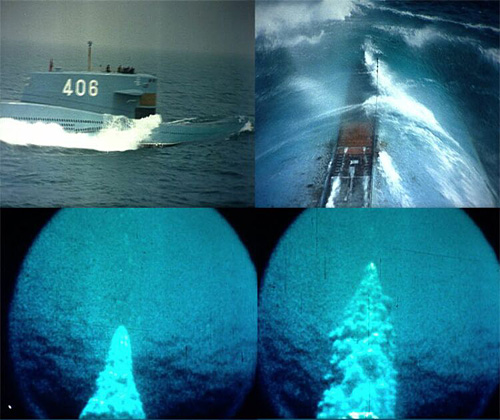

The images recorded during the JL-1 test launch from the Type 091 nuclear missile submarine. The top two images show the submarine carrying the missile submerging. The below two images taken by underwater camera show the missile being ejected from the submarine’s missile launch tube.图片记录JL-1从091型核导弹潜艇试射。前二幅图片潜艇携带导弹潜入水中。在下面两幅由水下照相机拍摄,显示导弹从潜艇的导弹发射管弹射出。
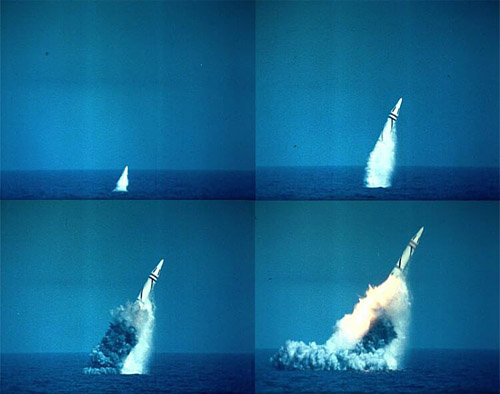
These images show the JL-1’s first-stage engine being ignited after the missile had emerged from the water.这些图像显示在导弹从水面脱离之后,JL-1第一级发动机点燃。
Design
The JuLang 1 missile uses a two-stage solid-propellant engine. The missile has a range of 1,700km (2,500km for JuLang 1A) with an accuracy of 700m CEP obtained from an inertial guidance system. It delivers a payload of a single warhead that weighs 600kg, which is believed be 200~1,000kT yield. The missile has no stabilising fins or wings. A Type 092 SSBN carries twelve JuLang 1 missiles in its missile tubes behind the sail.
设计
巨浪-1型导弹采用二级固体推进剂发动机。导弹射程1,700公里(巨浪-1A为2,500公里)采用惯性导航系统具有700米CEP精度。它递送一枚重600公斤的单一弹头负载,据信200~1,000 kT当量。导弹没有稳定翼或弹翼。092型SSBN在帆罩后的导弹发射管内携带十枚巨浪-1型导弹。

The JL-1 SLBM carries a single nuclear warhead and has a max range of 2,150km. This was increased to 2,500km on the improved JL-1A.JL-1 SLBM携带一枚单一核弹头和最大射程2,150公里。在改进的JL-1A上增加到2,500公里。
The JuLang 1 is stored and transported inside a cylinder missile tube, which is loaded onto the submarine at its homeport before departure. The missile is launched using ‘cold-launch’. Firstly the missile is ejected from the submarine missile tube using fuel gas, with the first-stage engine igniting after the missile has emerged from the water. Because the missile does not have establishing or controlling surfaces, it completely relies on the swinging nozzles of its first stage engine to maintain its course of flight. On the head of the second-stage there are three mini rocket motors to help the stage separate from the warhead.
在离开储藏点装填入潜艇前,巨浪-1型在圆形导弹筒内储存和运送。导弹发射采用‘冷-发射’。首先导弹被可燃气体从潜艇导弹发射管弹射,在导弹离开水面之后点燃第一级发动机。因为导弹没有稳定或控制翼面,它完全地依靠在第一级发动机的摆动喷嘴去维持它的飞行航线。在第二级上部有三台微型火箭发动机帮助该级和弹头分离。

The JL-1 SLBM carried inside a launch tube being loaded onto the Type 091 nuclear missile submarine. The submarine can carry 12 missiles.JL-1 SLBM在发射筒内携带装填到091型核导弹潜艇之内。潜艇能携带12枚导弹。
Launches
17 June 1981: Launch Site: Taiyuan (Wuzhai); Result: Success. Purpose: First land-based flight test from the launch pad.
7 January 1982: Launch Site: Taiyuan (Wuzhai); Result: Success. Purpose: Land-based flight test from the launch tube.
22 April 1982: Launch Site: Taiyuan (Wuzhai); Result: Success. Purpose: Land-based flight test from the launch tube.
7 October 1982: Launch Site: Bohai Sea Missile Range; Result: Failure. Purpose: First underwater launch from a Type 031 (Gulf class) diesel-electric missile submarine. The missile lost control shortly after take-off and was self-destructed.
12 October 1982: Launch Site: Bohai Sea Missile Range; Result: Success. Purpose: Underwater launch from a Type 031 (Gulf class) diesel-electric missile submarine.
28 September 1985: Launch Site: Bohai Sea Missile Range; Result: Failure. Purpose: Underwater launch from a Type 092 (Xia class) nuclear-powered missile submarine (SSBN).
15 September 1988: Launch Site: Bohai Sea Missile Range; Result: Success. Purpose: Underwater launch from a Type 092 (Xia class) nuclear-powered missile submarine (SSBN). This was the first successful JL-1 test from the Type 092 SSBN.
27 September 1988: Launch Site: Bohai Sea Missile Range; Result: Success. Purpose: Underwater launch from a Type 092 (Xia class) nuclear-powered missile submarine (SSBN). The second successful launch of the JL-2 from the Type 092 SSBN allowed the missile design to be finalised.
发射
1981年6月17日: 发射位置:太原(五寨(Wuzhai))结果:成功。目的:首次从发射台进行陆基飞行测试。
1982年1月7日: 发射位置:太原(五寨(Wuzhai));结果:成功。目的:从发射管进行陆基飞行测试。
1982年4月22日: 发射位置:太原(五寨(Wuzhai));结果:成功。目的:从发射管进行陆基飞行测试。
1982年10月7日: 发射位置:渤海导弹试验水域;结果:失败。目的:首次在水下从一艘031型(高尔夫级)柴电导弹潜艇发射。在起飞后不久导弹失去控制并自毁。
1982年10月12日: 发射位置:渤海导弹试验水域;结果:成功。目的:在水下从一艘031型(高尔夫级)柴电导弹潜艇发射。
1985年9月28日: 发射位置:渤海导弹试验水域;结果:失败。目的:在水下从一艘092型(夏级)核动力导弹潜艇(SSBN)发射。
1988年9月15日: 发射位置:渤海导弹试验水域;结果:成功。目的:在水中下从092型(夏级)核动力导弹潜艇(SSBN)发射。这是JL-1型从092型SSBN上首次成功测试。
1988年9月27日: 发射位置:渤海导弹试验水域;结果:成功。目的:在水下从092(夏级)核动力导弹潜艇(SSBN)进行的第二次JL-2型成功发射。092型SSBN携带的导弹获得设计定型。
Specifications
Configuration: Two-stage, solid propellant
Deployment: Submarine launch
Length: 10.70m
Diameter: 1.34m
Launch weight: 14,700kg
Range: 1,700km (JL-1); 2,500km (JL-1A)
Re-entry vehicle mass: 600kg
Warhead: One single 200~1,000kT
Guidance: Inertial + celestial + satellite guidance
Accuracy: CEP ~600m
规格
结构: 二级,固体推进剂
配置: 潜艇发射
长度: 10.70 米
直径: 1.34 米
发射重量: 14,700 公斤
射程: 1,700 公里(JL-1);2,500 公里(JL-1A)
再入运载具质量: 600 公斤
弹头: 单一 200~1,000 kT
制导: 惯性 + 天文 + 星形 制导
精度: CEP~600 米
Last update: 14 March 2009
最后更新: 2009年3月14日
上一篇:DongFeng 41 (CSS-X-10) Intercontinental Ballistic Missile 下一篇:JuLang-2 (CSS-NX-4) Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile
| DF-1 ballistic missile system
中国东风-1(DF-1)弹道导弹系统 |
| China’s first ballistic missile system, a licensed copy of the Soviet R-2 (SS-2 ‘Sibling’) short-range ballistic missile.... [2020-04-05] |
| B611 TACTICAL SURFACE-TO-SURFACE BALLISTIC MISSILE
中国B611战术地对地弹道导弹 |
| The B611 is the solid-fuel, surface-to-surface, short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) jointly developed by China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation (CASIC) and Turkish weapon manufacturer MKEK.... [2017-01-15] |
| DF-21/A/C(CSS-5 Mod1/2/3)medium-range ballistic missile
中国东风-21/A/C型中程弹道导弹 |
| The DF-21 is a two-stage, solid-fuel rocket, single-warhead medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) in the Dong Feng series developed by China Changfeng Mechanics and Electronics Technology Academy.... [2016-08-17] |
| DongFeng 31A (CSS-9 Mod-2) Intercontinental Ballistic Missil
中国DF-31A(CSS-9 Mod-2)洲际弹道导弹 |
| The DongFeng 31A (NATO reporting name: CSS-9 Mod-2) is a road-mobile, three-stage, solid-propellant intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), designed to carry a single 1,000kT thermal nuclear warhead.... [2016-01-04] |
